CLINICAL DERMATOLOGY
CLINICAL DERMATOLOGY
- Acne, melasma, and hyperpigmentation treatments
- Psoriasis, eczema, and vitiligo management
- Hair loss treatments – PRP therapy, mesotherapy, and advanced hair restoration
- Fungal infections, warts, urticaria, and keloid treatments
CLINICAL DERMATOLOGY TYPES
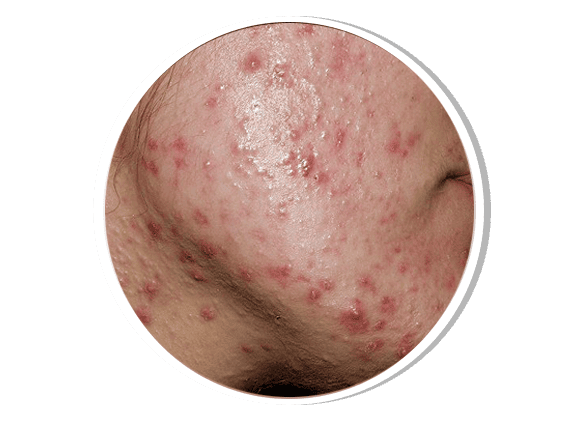
ACNE Dermatology
Acne is a common inflammatory skin disorder affecting the face, chest, back, and shoulders. It occurs due to excess sebum production, clogged pores, bacterial overgrowth (Cutibacterium acnes), and inflammation. It manifests as comedones (blackheads and whiteheads), papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts. Factors such as hormonal changes, genetics, diet, and stress can aggravate acne. Treatment options include topical retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, antibiotics, hormonal therapy, and advanced procedures like chemical peels and laser therapy.
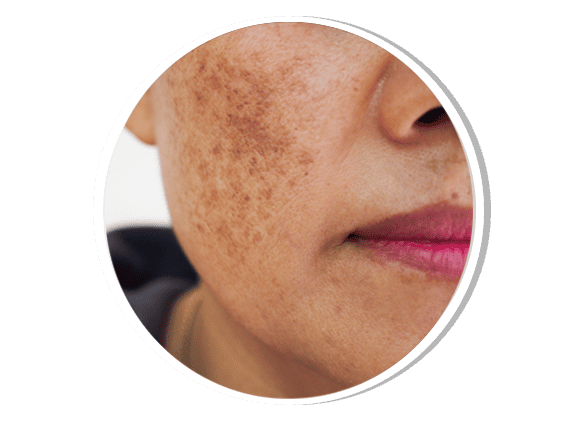

Melasma Dermatology
Melasma is a chronic pigmentary disorder characterized by brown or grayish patches, primarily on sun-exposed areas like the face. It is triggered by sun exposure, hormonal changes (pregnancy, oral contraceptives), and genetic predisposition. Treatment involves sun protection, topical depigmenting agents (hydroquinone, kojic acid, azelaic acid), chemical peels, and laser therapy for resistant cases.
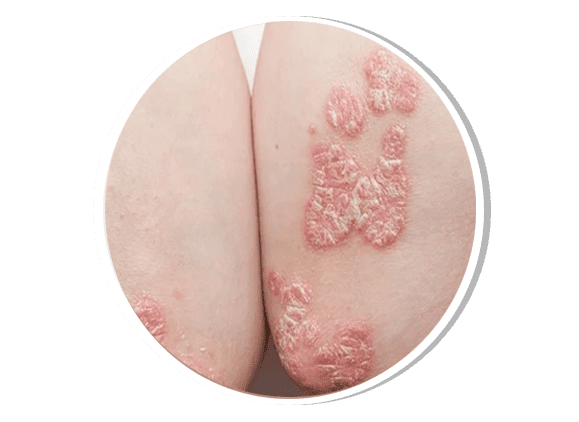
Psoriasis Dermatology
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes rapid skin cell turnover, leading to red, scaly plaques covered with silvery-white scales. It commonly affects the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back. Triggers include stress, infections, trauma, and certain medications. Types of psoriasis include plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, inverse psoriasis, pustular psoriasis, and erythrodermic psoriasis. Treatment includes topical corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, phototherapy, systemic immunosuppressants, and biologic therapy.
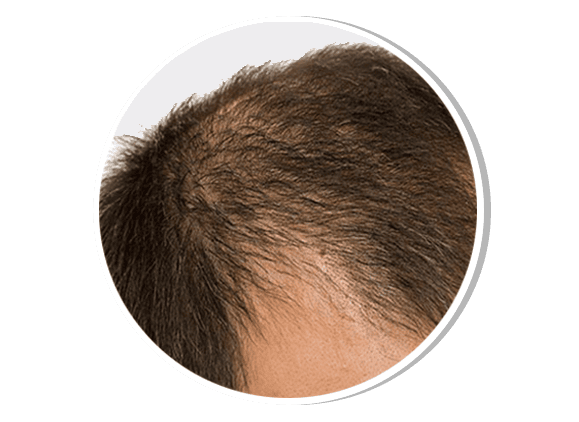
Androgenetic Alopecia (Male Pattern Baldness)
Androgenetic alopecia is a genetically determined progressive hair loss condition influenced by dihydrotestosterone (DHT), leading to miniaturization of hair follicles. It typically presents with a receding hairline and thinning at the crown. Treatment includes topical minoxidil, oral finasteride, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, low-level laser therapy, and hair transplantation.
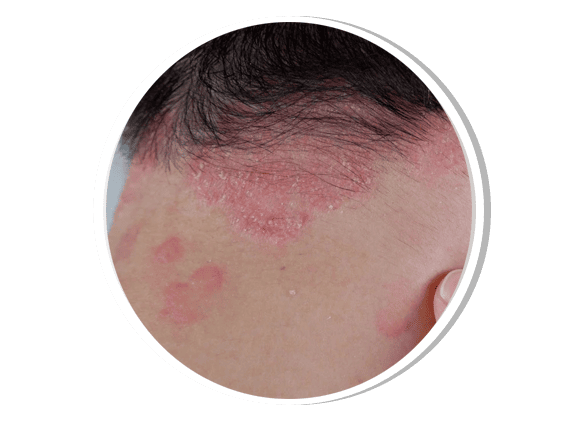
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin condition presenting with red, itchy, dry, and scaly skin, commonly affecting children and individuals with allergic tendencies. Triggers include allergens, irritants, weather changes, and stress. Treatment focuses on skin hydration, topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, antihistamines, and advanced biologic therapy for severe cases.
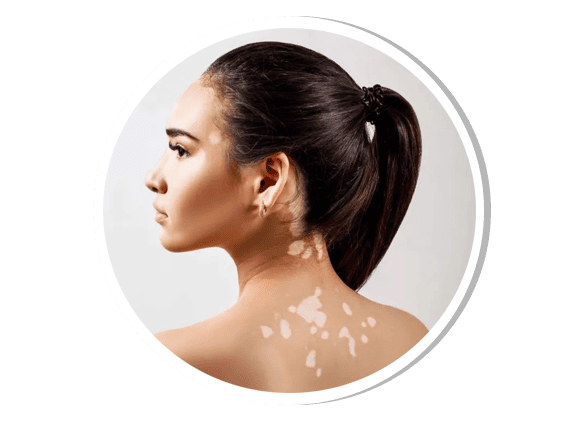

Vitiligo
Vitiligo is an autoimmune disorder characterized by depigmented white patches due to the destruction of melanocytes. It can be localized, segmental, or generalized. The exact cause is unknown but is linked to genetic, autoimmune, and environmental factors. Treatment includes topical steroids, calcineurin inhibitors, phototherapy, and surgical techniques like melanocyte transplantation in refractory cases.
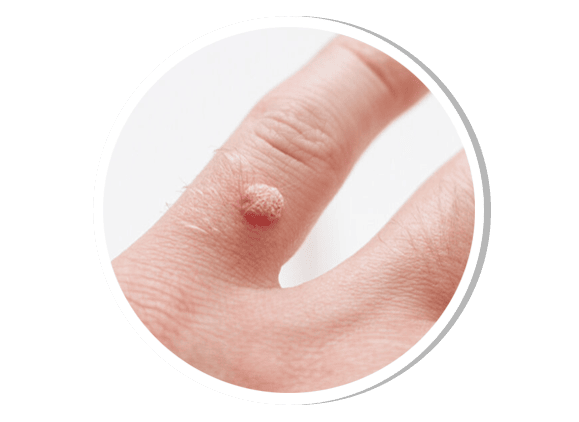
Warts
Warts are benign skin growths caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Types include:
Common warts (verruca vulgaris) – Rough, raised lesions on hands and fingers
Plantar warts – Thickened lesions on the soles of feet
Genital warts – Sexually transmitted HPV lesions
Treatment includes cryotherapy, electrocautery, laser therapy, and topical agents like salicylic acid and imiquimod.
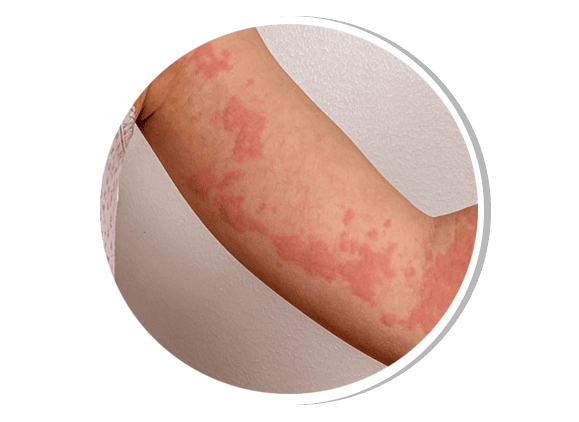
Urticaria (Hives)
Urticaria is a hypersensitivity reaction causing itchy, red, raised welts on the skin. It can be acute (lasting less than six weeks) or chronic. Triggers include allergens, medications, infections, stress, and autoimmune conditions. Treatment includes antihistamines, corticosteroids, and immunomodulators in refractory cases.
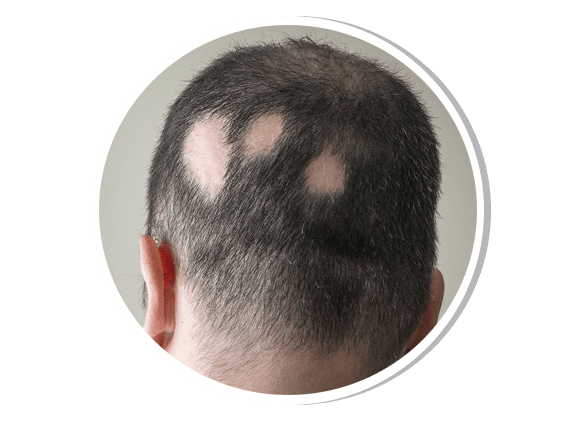
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition that results in sudden, patchy hair loss on the scalp, beard, or body. It occurs when the immune system attacks hair follicles. In some cases, it progresses to alopecia totalis (complete scalp hair loss) or alopecia universalis (total body hair loss). Treatment includes corticosteroids (topical, intralesional, systemic), immunomodulators, and JAK inhibitors in severe cases.
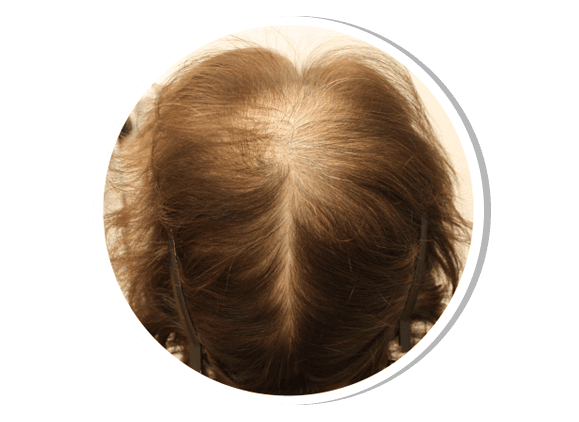

Female Pattern Androgenetic Alopecia
Female pattern hair loss (FPHL) is a diffuse thinning of hair over the crown and mid-scalp due to hormonal and genetic factors. Unlike male pattern baldness, the frontal hairline is usually preserved. Treatment includes topical minoxidil, hormonal therapy (spironolactone, oral contraceptives), PRP therapy, and hair restoration procedures.
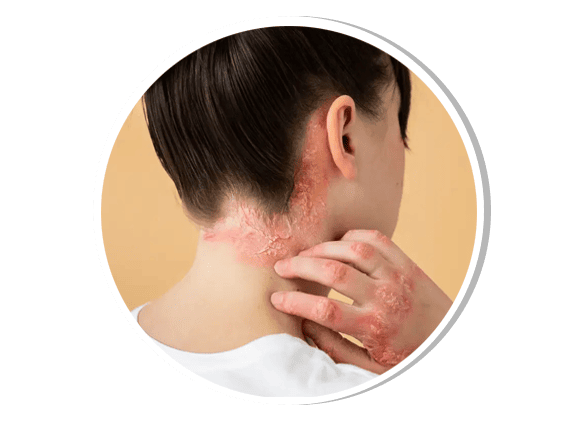
Fungal Infections (Dermatophytosis/Tinea)
Fungal infections are caused by dermatophytes, yeasts, or molds, affecting the skin, nails, and scalp. Common types include:
Tinea corporis (ringworm) – Circular scaly patches on the body
Tinea capitis – Scalp fungal infection leading to hair loss
Tinea pedis (athlete’s foot) – Itchy, peeling skin between toes
Tinea cruris (jock itch) – Groin fungal infection
Onychomycosis – Nail fungal infection causing thickened, discolored nails
Treatment involves topical and oral antifungal medications such as terbinafine, fluconazole, and itraconazole.
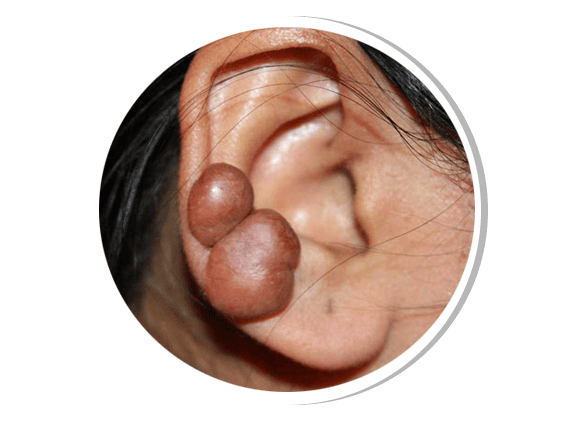
Keloid
A keloid is an excessive overgrowth of scar tissue that extends beyond the original wound site. It commonly occurs after surgery, trauma, piercings, or burns and is more prevalent in darker skin tones. Treatment includes corticosteroid injections, silicone gel sheets, laser therapy, cryotherapy, and surgical excision (with recurrence prevention strategies).
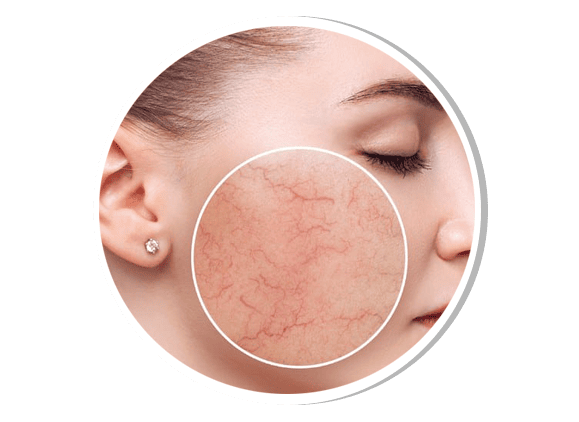
Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition presenting with persistent facial redness, flushing, visible blood vessels, and acne-like bumps. Triggers include heat, spicy food, alcohol, stress, and sunlight. Subtypes include erythematotelangiectatic, papulopustular, phymatous, and ocular rosacea. Treatment includes topical metronidazole, azelaic acid, oral doxycycline, and laser therapy.
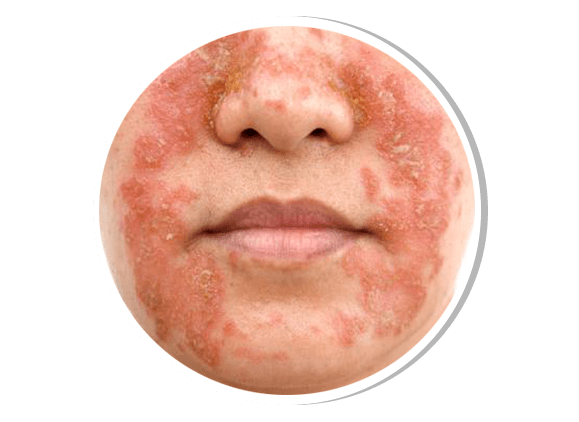
Topical Steroid Damage Facies
TSDF occurs due to prolonged, inappropriate use of potent topical corticosteroids, leading to skin thinning, increased sensitivity, redness, acneiform eruptions, and telangiectasia. Management involves gradual steroid withdrawal, supportive skincare, topical calcineurin inhibitors, and laser therapy for persistent vascular damage.
BOOK AN APPOINTMENT & YOU'RE DONE!
Looking for the best & quick dermatology treatments without a long waiting time?

